BODY
Health, Hygiene, Fitness, Energy
What It Takes To Lose A Pound
Unit of Weight | Approximate Calories | Approximate Kilojoules |
1 Pound of Fat | 3,500 | 14,644 |
A pound of body fat equates to approximately 3500 calories. So if you have a calorie deficit of 500 calories (meaning that you burn 500 calories more than you eat each day) you would lose approximately one pound per week:
500 x 7 = 3,500
It's easy to see that a calorie deficit of 1000 calories
would mean that you'd lose approximately two pounds per week. And that's a good number to remember, because two pounds a week is commonly accepted as the maximum rate of weight loss that is healthy.
It's easy to see that a calorie deficit of 1000 calories
would mean that you'd lose approximately two pounds per week. And that's a good number to remember, because two pounds a week is commonly accepted as the maximum rate of weight loss that is healthy.
 |
| Muscular System |
Get Stronger. 1
Do Compound Exercises. 3
Train Your Legs. 4
Do Full Body Workouts. 5
Get Recovery. 6
Eat Whole Foods. 7
Eat More. 8
Gain Weight. 9
Get Protein. 10
 |
| a pound of fat is about the size of a mug |
ANATOMY
 |
| Nervous System |
 |
| Skeletal System |
 |
| Endocrine System |
Adrenal Glands
The adrenal glands are triangular shaped endocrine glands. They are located over the top of the kidneys. Their main function is the release of hormones when the body is under stress. These hormones are released by synthesis of corticosteroids and catecholamines that include cortisol and adrenaline. You can read more on functions of adrenal gland.
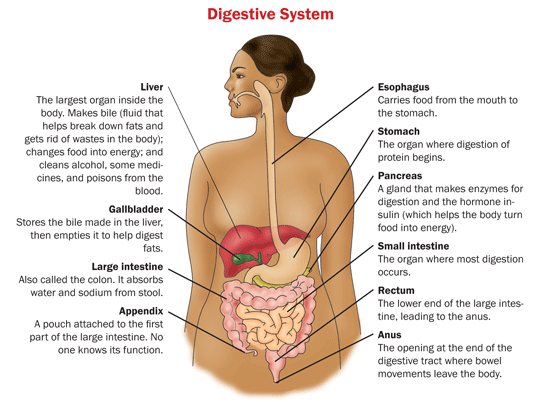
Appendix
The appendix is also known as the vermiform appendix, cecal appendix or vermix. The appendix is a blind ended tube that is connected to the cecum. It is developed embryologically from the cecum, that is, a pouch like structure of the colon. The appendix location is near the junction of small intestine and the large intestine. Traditionally, there are no known appendix functions. People who have got their appendix removed have never reported any kind of problem with their health.
Bladder
The bladder or urinary bladder is the organ where the excreted urine by the kidneys is collected before being disposed off by urination. The bladder is a muscular organ that is elastic (distensible) in nature. The bladder is located on the pelvic floor. In males, the base of the bladder is between the rectum and pubic symhysis. In females, it is below the uterus and above the vagina. In infants and young children, the bladder is located in the abdomen even if it is empty. You can read more on endocrine system diagram.
Brain
The brain is the most important organ of the human body. It is just like the captain of the ship, that controls each and every part of the human body. The brain is the center of the nervous system and is the most complex of all human body internal organs. The brain controls our sense of vision, hearing, taste, smell, balance and feeling. There are 15 to 33 billion neurons in the brain that depend on the age and sex of an individual. The brain controls the internal organs of the human body, either by secretion of chemicals or activation the muscles. The human brain is what differentiates man from other vertebrates making us the most intelligent of all species. You can read more on how the brain works and the brain parts and functions along with human brain diagram for more information.
Esophagus
The esophagus or gullet is a long muscular tube that passes from the pharynx into the stomach. The word esophagus is derived from a Greek word oisophagos, that means 'entrance for eating'. The esophagus connects the mouth to the stomach and is about 25 to 30 cm long. You can read more on esophagus function.
Gall bladder
The gallbladder, also known as the cholecyst is one of the small internal organs of the human body. It helps in digestive process and the bile produced in the liver is stored in the gall bladder. It is located in the concavity of liver that is called as the gallbladder fossa. The length of the gall bladder is about 8 cm in adults when fully distended. You can read more on where is the gallbladder located in the body.
Heart
The human heart is second most important internal human organ after the brain. It is muscular organ whose main function is to pump oxygenated blood throughout the body through blood vessels. This pumping is carried out by repeated, rhythmic contractions. The human heart beats 72 times per minute on an average and weighs about 250 g to 300 g in females and 300 g to 350 g in males. You can read in detail about how the heart works and go through the detailed heart diagram.
Intestines
The intestines or bowels are a segment of alimentary canal. The intestines extend from the stomach to the anus and is divided into small intestine and large intestine. The small intestine is divided into duodenum, jejunum and ileum. The large intestine is divided into the cecum and colon. You can read more in detail about the large intestine anatomy and small intestine anatomy.
Kidney
There are two kidneys in the human body. They are the most important part of the urinary system. The function of the kidneys is regulation of electrolytes, maintaining of acid-base balance, regulation of blood pressure, production of urine, etc. The kidneys help excrete urea and ammonium from the body and reabsorb water, glucose and amino acids. Calcitriol, renin and erythropoietin hormones are produced by the kidney. You can read more on histology of kidney and how does the kidney work.
Liver
One of the most vital internal human organ is the liver. The liver is an absolute necessity for survival and no individual can survive without the liver. The liver carries out many functions that includes detoxification of blood, production of biochemicals for digestion and protein synthesis. You can read more on digestive tract diagram.
Lungs
Lungs are the most important human body internal organs for respiration. In humans, there are two lungs located in the chest on either side of heart. The function of the lungs is to transport atmospheric oxygen into the bloodstream and release of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere from the blood. You can read more on lungs.
Ovaries
The ovaries are internal organs of the female body. They are ovum producing reproductive organs that are present in pairs. The ovaries are located in the lateral wall of the pelvis. This region is called the ovarian fossa that is present below the external iliac artery and in front of the internal iliac artery and ureter. You can read more on ovaries.
Pancreas
The pancreas are gland organs of the endocrine system and digestive system. The pancreas produce the most important hormones like insulin, glucagon and somatostatin. They also produce pancreatic juice that contains digestive enzymes. If the pancreas do not function normally, it may lead to diabetes mailitus. You can read more on function of pancreas and pancreas problems.
Parathyroid gland
The small endocrine glands are parathyroid glands that are present in the neck. These parathyroid glands are located below the thyroid glands. They produce the parathyroid hormones and control the amount of calcium in the blood and within the bones. You can read more on throat glands.
Pituitary gland
The pituitary gland is also a part of the endocrine system. It is just about the size of peas and are located at the base of the brain in the small bony cavity covered by a dural fold. The pituitary gland is the master gland that secretes hormones for regulation of homeostasis. It also secretes hormones that stimulate other glands for secretion of hormones. You can read more on glands in the human body and pituitary gland function.
Prostate gland
The prostate gland is a part of the male reproductive system. The function of prostate gland is to secrete a milky fluid that contains semen, spermatozoa and seminal vesicle fluid. It also controls the flow of urine during ejaculation. You can read more about prostate gland anatomy and prostate gland function.
Spleen
The spleen is the most important internal human organ with respect to the immune system. The spleen is located in the left upper quadrant of the abdomen. The function of the spleen is to remove old red blood cells and recycle iron. The spleen in an adult human body is about 11 cm in length. You can read more on spleen function in immune system.
Stomach
The muscular, hollow bag in the alimentary canal is the stomach. The stomach is the primary organ of the digestive system that is involved in the second phase of food digestion. The location of the stomach is between the esophagus and small intestine. The function of the stomach is to churn food with help of smooth muscular contortions, secrete protein digesting enzymes and strong aids for food digestion. It then passes the partially digested food towards the small intestine.
Testicles
The testicles are present in males and are the generative glands of the male body. The testicles produce sperms and male sex hormones like testosterone. There are two testes in a healthy male. You can read more on the human reproductive system.
Thymus gland
The thymus glands are specialized organs of the immune system. The thymus gland is located in front of the heart and behind the sternum. The function of the thymus gland is production of T-lymphocytes that are very important for adaptive immune system.
Thyroid gland
The largest endocrine gland of the human body is the thyroid gland. The thyroid gland is located in the neck below the Adam's apple. The hypothalamus and pituitary glands controls the thyroid gland. The thyroid glands helps control the use of energy in the body, makes proteins and also controls the sensitivity of the body towards other hormones. You can read more on thyroid gland function.
Uterus
The uterus or womb is the most important part of the female reproductive system. The uterus is internally connected to the fallopian tubes on each side and open into the vagina at one end. The uterus is the organ where the fetus develops during gestational period. The other functions of the uterus is to provide support and structural integrity to the bladder, bowel and pelvic organs. It is a very important part of sexual response in females as it directs the blood flow to the pelvis, ovaries, vagina, labia and clitoris. The uterus is also very important as it accepts the ovum from the fallopian tube and implants it into the endometrium wall. Here, it nourishes the ovum till it is fertilized. And unfertilized ovum along with the blood and endometrial lining is pushed out of the uterus. Thus, leading to the beginning of menstrual cycle every month in women after attaining puberty.
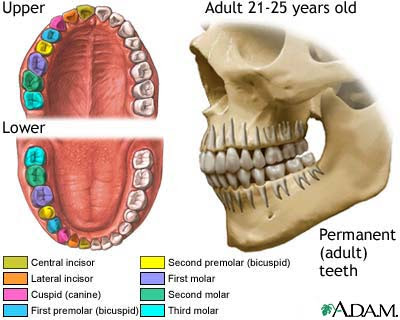
ORAL CAVITY